что такое нон планар
non-planar
Смотреть что такое «non-planar» в других словарях:
Planar chirality — is the special case of chirality for two dimensions.This term is most frequently used in chemistry contexts, e.g., for a chiral molecule lacking an asymmetric carbon atom, but possessing two non coplanar rings that are each dissymmetric and which … Wikipedia
Planar graph — Example graphs Planar Nonplanar Butterfly graph K5 The complete graph K4 … Wikipedia
Non-Euclidean geometry — Behavior of lines with a common perpendicular in each of the three types of geometry Non Euclidean geometry is the term used to refer to two specific geometries which are, loosely speaking, obtained by negating the Euclidean parallel postulate,… … Wikipedia
Planar ternary ring — In mathematics, a planar ternary ring (PTR) or ternary field is an algebraic structure (R,T), where R is a non empty set, and T colon R^3 o R is a mapping satisfying certain axioms. A planar ternary ring is not a ring in the traditional sense.… … Wikipedia
Non-uniform circular motion — Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law History of classical mechanics  … Wikipedia
Non-inertial reference frame — A non inertial reference frame is a frame of reference that is under acceleration.[1] The laws of physics in such a frame do not take on their most simple form, as required by the theory of special relativity.[2][3] To explain the motion of… … Wikipedia
Non-invasive intracranial pressure measurement methods — Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is one of the major causes of secondary brain ischemia that accompanies a variety of pathological conditions, most notably, traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, and intracranial hemorrhages. However, aside… … Wikipedia
Non-Euclidean crystallographic group — In mathematics, a non Euclidean crystallographic group, NEC group or N.E.C. group is a discrete group of isometries of the hyperbolic plane. These symmetry groups correspond to the wallpaper groups in euclidean geometry. A NEC group which… … Wikipedia
Mechanics of planar particle motion — Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law History of classical mechanics … Wikipedia
Centrifugal force (planar motion) — In classical mechanics, centrifugal force (from Latin centrum center and fugere to flee ) is one of the three so called inertial forces or fictitious forces that enter the equations of motion when Newton s laws are formulated in a non inertial… … Wikipedia
non-planar
1 non-planar
2 non-planar
3 non-planar
4 non-planar
5 non-planar
6 non-planar
См. также в других словарях:
Planar chirality — is the special case of chirality for two dimensions.This term is most frequently used in chemistry contexts, e.g., for a chiral molecule lacking an asymmetric carbon atom, but possessing two non coplanar rings that are each dissymmetric and which … Wikipedia
Planar graph — Example graphs Planar Nonplanar Butterfly graph K5 The complete graph K4 … Wikipedia
Non-Euclidean geometry — Behavior of lines with a common perpendicular in each of the three types of geometry Non Euclidean geometry is the term used to refer to two specific geometries which are, loosely speaking, obtained by negating the Euclidean parallel postulate,… … Wikipedia
Planar ternary ring — In mathematics, a planar ternary ring (PTR) or ternary field is an algebraic structure (R,T), where R is a non empty set, and T colon R^3 o R is a mapping satisfying certain axioms. A planar ternary ring is not a ring in the traditional sense.… … Wikipedia
Non-uniform circular motion — Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law History of classical mechanics  … Wikipedia
Non-inertial reference frame — A non inertial reference frame is a frame of reference that is under acceleration.[1] The laws of physics in such a frame do not take on their most simple form, as required by the theory of special relativity.[2][3] To explain the motion of… … Wikipedia
Non-invasive intracranial pressure measurement methods — Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is one of the major causes of secondary brain ischemia that accompanies a variety of pathological conditions, most notably, traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, and intracranial hemorrhages. However, aside… … Wikipedia
Non-Euclidean crystallographic group — In mathematics, a non Euclidean crystallographic group, NEC group or N.E.C. group is a discrete group of isometries of the hyperbolic plane. These symmetry groups correspond to the wallpaper groups in euclidean geometry. A NEC group which… … Wikipedia
Mechanics of planar particle motion — Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law History of classical mechanics … Wikipedia
Centrifugal force (planar motion) — In classical mechanics, centrifugal force (from Latin centrum center and fugere to flee ) is one of the three so called inertial forces or fictitious forces that enter the equations of motion when Newton s laws are formulated in a non inertial… … Wikipedia
non-planar
Смотреть что такое «non-planar» в других словарях:
Planar chirality — is the special case of chirality for two dimensions.This term is most frequently used in chemistry contexts, e.g., for a chiral molecule lacking an asymmetric carbon atom, but possessing two non coplanar rings that are each dissymmetric and which … Wikipedia
Planar graph — Example graphs Planar Nonplanar Butterfly graph K5 The complete graph K4 … Wikipedia
Non-Euclidean geometry — Behavior of lines with a common perpendicular in each of the three types of geometry Non Euclidean geometry is the term used to refer to two specific geometries which are, loosely speaking, obtained by negating the Euclidean parallel postulate,… … Wikipedia
Planar ternary ring — In mathematics, a planar ternary ring (PTR) or ternary field is an algebraic structure (R,T), where R is a non empty set, and T colon R^3 o R is a mapping satisfying certain axioms. A planar ternary ring is not a ring in the traditional sense.… … Wikipedia
Non-uniform circular motion — Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law History of classical mechanics  … Wikipedia
Non-inertial reference frame — A non inertial reference frame is a frame of reference that is under acceleration.[1] The laws of physics in such a frame do not take on their most simple form, as required by the theory of special relativity.[2][3] To explain the motion of… … Wikipedia
Non-invasive intracranial pressure measurement methods — Increased intracranial pressure (ICP) is one of the major causes of secondary brain ischemia that accompanies a variety of pathological conditions, most notably, traumatic brain injury (TBI), stroke, and intracranial hemorrhages. However, aside… … Wikipedia
Non-Euclidean crystallographic group — In mathematics, a non Euclidean crystallographic group, NEC group or N.E.C. group is a discrete group of isometries of the hyperbolic plane. These symmetry groups correspond to the wallpaper groups in euclidean geometry. A NEC group which… … Wikipedia
Mechanics of planar particle motion — Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law History of classical mechanics … Wikipedia
Centrifugal force (planar motion) — In classical mechanics, centrifugal force (from Latin centrum center and fugere to flee ) is one of the three so called inertial forces or fictitious forces that enter the equations of motion when Newton s laws are formulated in a non inertial… … Wikipedia
non-planar network
1 non-planar network
2 non-planar network
3 non-planar
4 non-planar
5 неплоская схема
См. также в других словарях:
Network analysis (electrical circuits) — Linear Network Analysis Elements … Wikipedia
Spatial network analysis software — are computer tools used to prepare various graph based analysis of spatial networks. They stem from the research field of space syntax in the domain of architecture, although they can now be used to analyse road networks over an entire… … Wikipedia
Mechanics of planar particle motion — Classical mechanics Newton s Second Law History of classical mechanics … Wikipedia
Centrifugal force (planar motion) — In classical mechanics, centrifugal force (from Latin centrum center and fugere to flee ) is one of the three so called inertial forces or fictitious forces that enter the equations of motion when Newton s laws are formulated in a non inertial… … Wikipedia
Dependency network — Contents 1 Importance 2 Overview 3 The activity dependency networks … Wikipedia
Graph coloring — A proper vertex coloring of the Petersen graph with 3 colors, the minimum number possible. In graph theory, graph coloring is a special case of graph labeling; it is an assignment of labels traditionally called colors to elements of a graph… … Wikipedia
Distributed element filter — Figure 1. A circuit featuring many of the f … Wikipedia
ISO 10303 Application Modules — The STEP Application modules define common building blocks to create modular Application Protocols (AP) within ISO 10303. Higher level modules are built up from lower level modules. The modules on the lowest level are wrappers of concepts,… … Wikipedia
Théorème de Robertson-Seymour — En mathématiques, et plus précisément en théorie des graphes, le théorème de Robertson–Seymour (parfois également appelé le théorème des mineurs, et connu, avant qu il soit démontré, sous le nom de conjecture de Wagner), est un théorème démontré… … Wikipédia en Français
Nowhere-zero flow — In graph theory, nowhere zero flows are a special type of network flow which is related (by duality) to coloring planar graphs. Let G = (V,E) be a directed graph and let M be an abelian group. We say that a map is a flow or an M flow if the… … Wikipedia
Photonic metamaterial — Electromagnetism Electricity · … Wikipedia
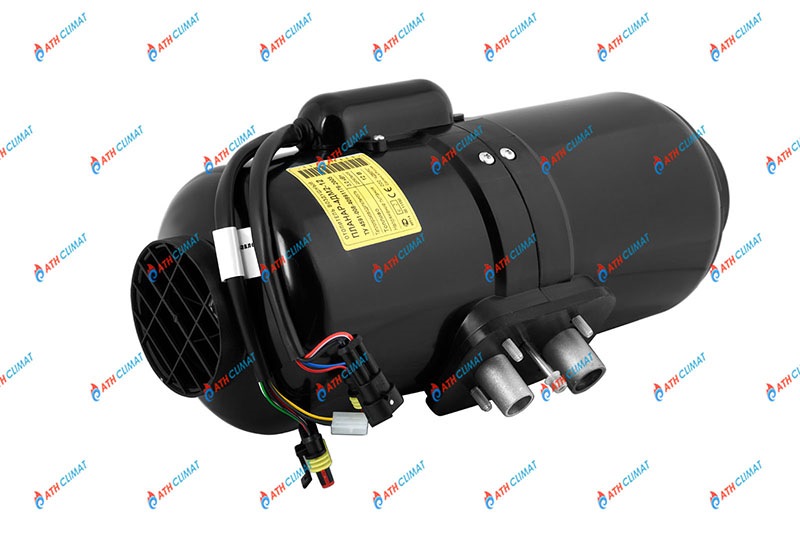
Принцип работы воздушного отопителя Планар–4ДМ2–12, 24
Сегодня мы с вами поговорим о работе автономного воздушного отопителя Планар – 4ДМ2-12,24, рассмотрим его устройство и принципах работы. Эти устройства весьма полезны и практичны не только для практически постоянной жизни в своем автомобиле, но и для поддержании оптимального температурного режима в будке, для обеспечения сохранности перевозимого груза. Применений такому воздушному отопителю можно найти массу, тем более он предельно прост в установке и эксплуатации.
В основе принципов работы воздушных отопителей Планар – 4ДМ2-12, 24 лежит использование теплоты сгорания топлива в специальной камере, которая снаружи обдувается потоком воздуха от вентилятора, обогревая полезное пространство. Ничего сложного, не правда ли?
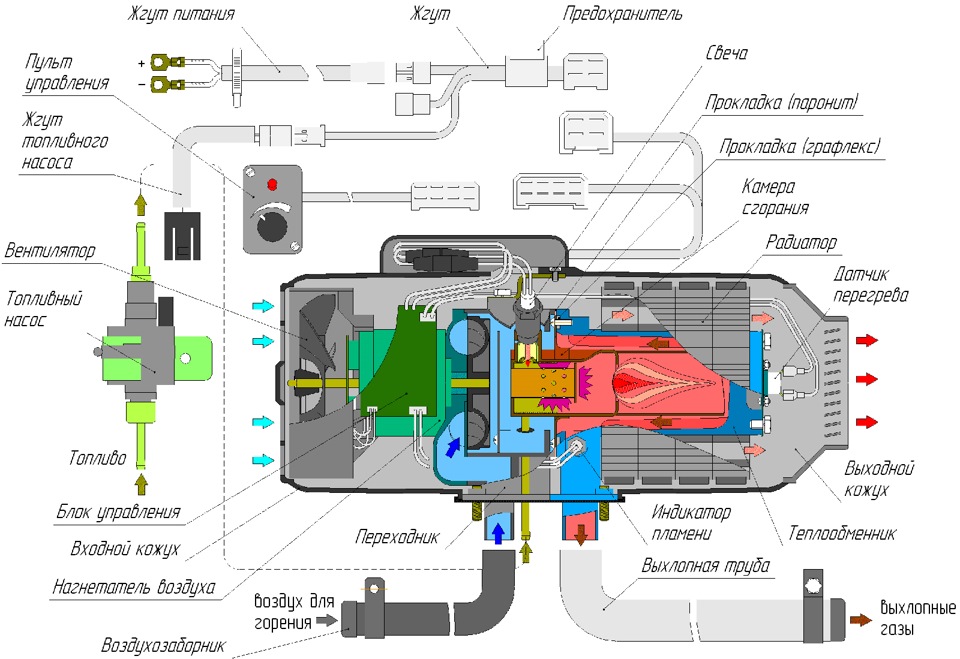
Но за такой простотой принципа работы, стоит немалое количество систем выполняющих контроль, управление, индикацию по всем сторонам работы устройства. Для того чтобы нам это лучше понять, посмотрим на схематический разрез воздушного отопителя Планар – 4ДМ2 – 12, 24:
Приобрести этот отопитель, а также практически все запчасти к нему, вы сможете в нашем интернет-магазине Athclimat.ru
Начнем, будем идти слева на право постепенно разбирая все комплектующие и рассказывая для чего они применяются в процессе работы.
Жгуты питания топливного насоса и провода – это как понятно из названия элемент системы отопителя, обеспечивающий питание электрических элементов, а также передача сигнала от пультов управления, блоков управления и тп.
Пульт управления – применяется для управления отопителем, включения-выключения, индикации ошибок и режимов работы. В воздушных отопителях Планар всей серии используются два варианта пультов управления – обычный и с ЖК-экраном. Последний позволяет выполнять более обширную настройку режимов работы, индикацию ошибок и выбранных параметров. Устанавливают обычно его непосредственно в салоне, чтобы обеспечить быстрый доступ водителю к управлению отопителем.
Топливный насос – предназначен для подкачки топлива к отопителю с топливного бака и поддержанию нужного давления. Управление им производит блок управления, он назначает необходимые режимы работы, тайминг и другие параметры, для обеспечения наибольшей производительности и стабильности работы.
Блок управления – «мозг» всей системы отопителя, предназначен для контроля и организации правильной работы всего отопителя, он «следит» за корректностью работы и горения топлива, температурным режимом устройства не допуская перегревов и опасных ситуаций. Также он контролирует и посредством пульта управления отображает ошибки в работе устройства.
Камера сгорания – элемент отвечающий за правильное сгорание топлива и его максимальную теплоотдачу теплообменнику.
Теплообменник – специально спроектированная часть воздушного отопителя, которая максимально эффективно производит поглощение тепла от сгорания топлива и отдает его нагреваемому воздуху, который продувается через теплообменник вентилятором.
Вентилятор с деталями воздуховодов – производит забор холодного воздуха и нагнетание его через теплообменник, тем самым нагревая его и увеличивая производительность отопителя, в плане обогрева.
Датчик перегрева – выполняет роль своеобразного предохранителя, который дает сигнал блоку управления в случае перегрева самого отопителя, не допуская аварийных ситуаций.
Свеча накала – отвечает за своевременный и надежный поджог топлива.
Индикатор пламени – датчик отвечающий за сигнализации наличия пламени в камере сгорания.
Процесс запуска и работы воздушного отопителя Планар 4ДМ2-12,24
Сейчас рассмотрим более детально процесс запуска и работы Планар 4ДМ2 – 12,24. При включении отопителя в работу, блок управления производит тестирование всех важных для работы компонентов:
• Топливного насоса
• Вентилятора
• Датчиков температуры, перегрева, индикатора пламени
• Свечи
Если какой либо компонент из вышеназванных неисправен, то блок управления выдаст ошибку и отопитель не запустится. Если тестирование прошло отлично, то блок управления включает вентилятор и свечу накала, которая в течении заданного времени набирает необходимую температуру для поджога топлива.
После истечения времени для нагрева свечи, блок управления подает сигнал для включения топливного насоса, происходит зажигание топливной смеси. Если по каким либо причинам топливо не воспламенилось, то отопитель повторит попытку запуска 2 раза, после чего выдаст ошибку. В положительном случае после получения стабильного горения в камере, блок управления отключает свечу накала и за наличием пламени в камере сгорания следит индикатор пламени.
Процесс работы контролируется блоком управления, согласно тем настройкам режимов работы, который задает пользователь с пульта управления. В блок управления заложена программа с комбинацией разных параметров на пульте, он автоматически контролирует силу пламени, управляет вентилятором и тп. Датчик перегрева же контролирует температуру прибора, если она превысит допустимые значения – горение топлива прекратится. Также блок управления следит за напряжением бортовой сети и при значениях ниже 10В, он прекратит свою работу.
При выключении, сначала прекращается горение в камере сгорания, затем происходит вентиляция – охлаждение камеры сгорания, после чего отопитель полностью прекращает работу.